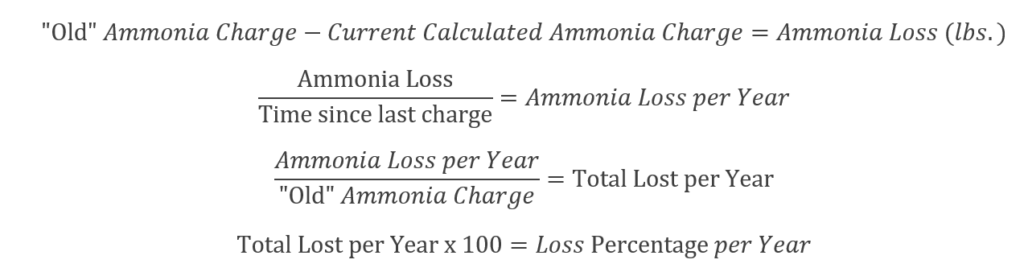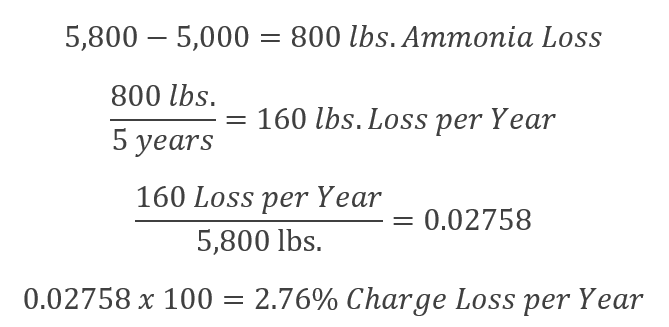The issue: A facility with an ammonia refrigeration system notes that their HPR level is rather low, and they are considering ordering some ammonia to get back to the levels they “used to have.” The thinking is that they need to add to the ammonia charge to make up for ammonia that was lost over the years.
Before you go too far, a good question to ask is: Did I lose ammonia? Or is it just somewhere else in my system?
What if you didn’t lose it?
Did you add equipment without your MOC addressing if this required an inventory adjustment? Did you change recirculator vessel levels which make the HPR look low even though the ammonia is still out in the system? Has someone been mucking with the HXV’s or TXV’s, so you are “brining” coils? These are common issues, but the most likely culprit is seasonal variation.
If it’s August in Texas, it’s likely that your system is running about as hard as it will ever run. That means that the NH3 isn’t just hanging out in your vessels, but out in the various heat exchangers (and their piping) doing its job. The “good old boy” method of testing this was to wait until the cool of the night, shut down the liquid feed to your “load,” and check the vessel levels after the NH3 came back.
A more “modern” method is to use an inventory spreadsheet and adjust the levels in the heat exchangers to reflect the summer load. The intricacies of doing either of these are better dealt with in the real world rather than a blog-post, so let’s assume you have already checked this and you actually do need ammonia. (Note: if you need assistance with either of the above, we can certainly assist you, just give us a call)
Ok, maybe we did lose it!
If you look into the situation and find out that you actually do need ammonia, there are a few considerations you should think of BEFORE you order that truck and start preparing for delivery.
- Figure out how much. Use an inventory spreadsheet (or have an engineer do it for you) to figure out how much ammonia you need to get back to your “normal” level.
- Review your charging SOP with the refrigeration team to make sure you are all on the same page. This isn’t something you should be doing often so take this opportunity to review, validate, and TRAIN on this procedure.
- Document where you think that ammonia went! For most facilities this is just calculating your “leak” rate. This is your “justification” that you are replacing lost ammonia, not adding to your intended inventory level.
Justifying the charge
Assuming you didn’t have some sort of incident that clearly explains why you need ammonia, we should figure out how to justify the amount we’re adding. Most losses are easily justified by establishing a “loss rate” and comparing it to accepted norms. This acceptable loss would be caused by normal maintenance, auto-purgers, and fugitive emissions.
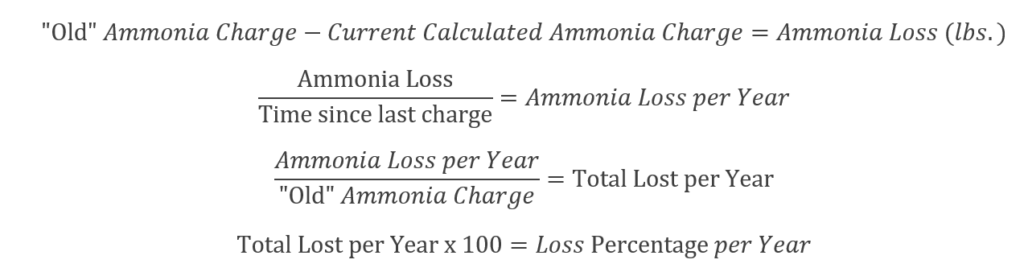
In my opinion, anything less than 5% is good. 2-3% is excellent. For what it’s worth, the IIAR has stated that up to 10% loss a year is “reasonable.”
A loss rate of 3% or less a year can easily be explained from normal maintenance, auto-purgers, and fugitive emissions.
This is easier to explain with a worked example from a friend. In this case, their inventory level is supposed to be 5,800lbs. When they updated their inventory sheet to reflect the actual conditions at the facility, they saw a calculated current charge of 5,000lbs reflecting an 800 pound loss. That loss occurred since their last charge 5 years ago.
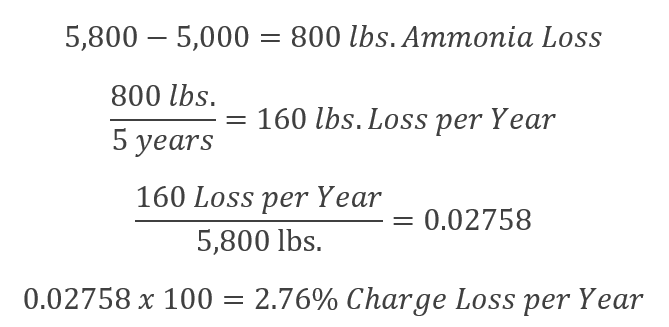
This percentage is easily explainable from maintenance and other fugitive emissions, and it’s also quite reasonable.
If you take the time to figure out the math above, and then document your calculations to justify your NH3 charge, it helps avoid unpleasant assumptions on the part of the EPA and OSHA in any future inspections.
If an auditor comes in and sees an ammonia delivery receipt, a documented rationale why the ammonia was needed, the SDS of the chemical charged, and you have a compliant charging procedure, it would be very unlikely that the charging process would be questioned further.
Of course, if your math shows a high leak rate, then you had better get an incident investigation going and figure out what’s wrong!
P.S. – To assist in this effort, Scott updated the Ammonia Inventory example template has been updated to help automate this process. Just enter the old value, newly measured value, and time (in months) since last charging and you have a 1-page report on the % loss per year. We hope this helps. The file can be located at: \ PSM-RMP Program Templates \ 03 – Process Safety Information \ Optional Resources \